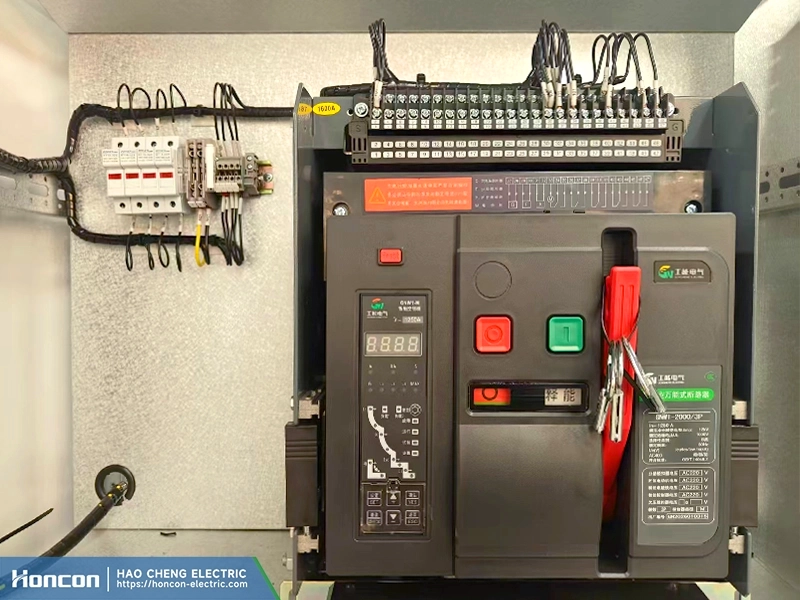
Low voltage withdrawable switchgear contacts are one of the most critical components in low voltage switchgear assemblies. As the primary electrical connection between withdrawable units and the main busbar system, low voltage withdrawable switchgear contacts directly affect system safety, operational stability, and long-term reliability.
In industrial power distribution systems, low voltage withdrawable switchgear contacts must maintain stable electrical performance under continuous rated current, repeated insertion cycles, and short-circuit stress. Poor contact performance can lead to abnormal temperature rise, increased power loss, and even equipment shutdown.
The Role of Low Voltage Withdrawable Switchgear Contacts
Low voltage withdrawable switchgear contacts serve as the primary interface between the withdrawable drawer unit and the fixed power distribution system. These contacts must:
Carry rated operating current continuously
Maintain low and stable contact resistance
Withstand short-circuit current during fault conditions
Ensure reliable electrical connection after multiple insertions and withdrawals
Because low voltage withdrawable switchgear contacts are located in the primary circuit, any degradation in contact quality directly impacts system continuity and electrical safety.
Key Performance Requirements for Withdrawable Switchgear Contacts
Rated Current Carrying Capability
Low voltage withdrawable switchgear contacts must be designed to carry rated current without excessive temperature rise. Proper contact material selection, contact surface treatment, and optimized contact pressure are essential to reduce resistance and prevent overheating.
Short-Circuit Withstand Performance
Although industrial withdrawable switchgear contacts usually only need to withstand short-circuit current for several milliseconds until circuit breaker tripping, high-quality low voltage withdrawable switchgear contacts are often tested to 50kA / 1s short-time withstand current. This provides additional safety margin and demonstrates superior mechanical and electrical robustness.
Mechanical Durability and Repeated Insertion
Repeated insertion and withdrawal can gradually affect contact alignment and surface condition. Low voltage withdrawable switchgear contacts must maintain stable contact pressure and low resistance throughout their service life to ensure long-term reliability.
Common Causes of Contact Overheating and Failure
In real-world projects, overheating and burning of withdrawable switchgear contacts are common issues. Typical root causes include:
Improper installation or insufficient insertion depth
Contact misalignment or uneven contact pressure
Surface oxidation or mechanical wear
Poor maintenance practices
Incorrect selection of low voltage withdrawable switchgear contacts for system short-circuit levels
These factors increase contact resistance, leading to localized heating, excessive temperature rise, and potential damage to switchgear components.
Different Contact Structures and Application Scenarios
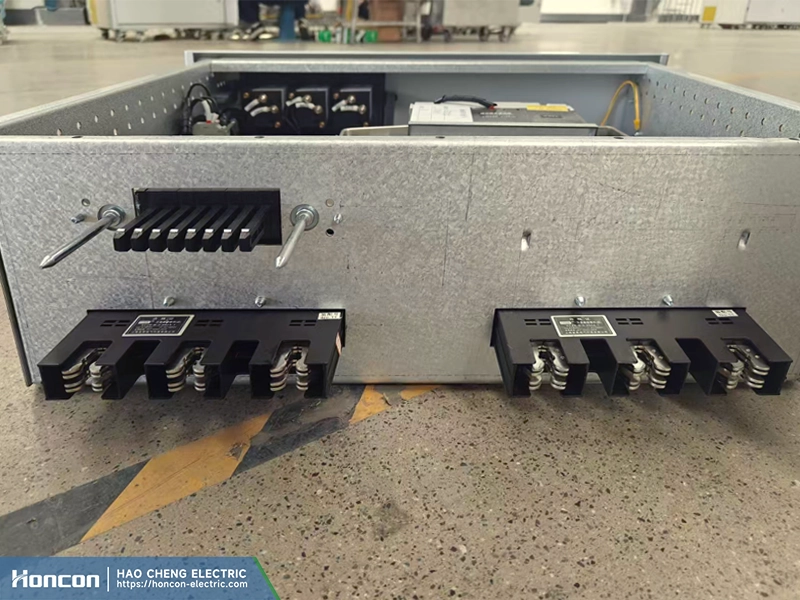
Traditional B-Type and MW Drawer Contacts
Traditional designs often use insertion depth gauges to ensure proper engagement. These low voltage withdrawable switchgear contacts rely on mechanical positioning to achieve stable electrical contact.
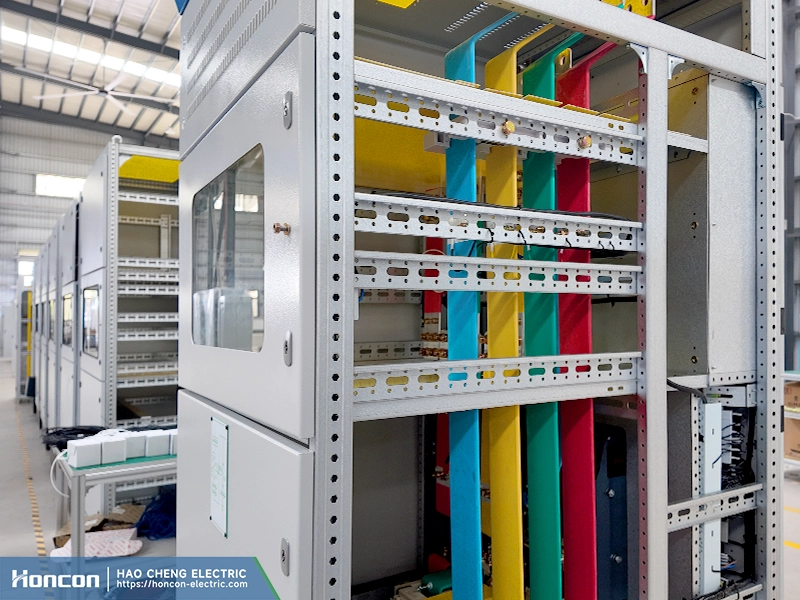
OKKEN Double-Clip Bidirectional Contacts
Modern OKKEN-type designs use double-clip bidirectional contact structures. This configuration improves contact stability, enhances current sharing, and reduces the risk of uneven contact pressure in withdrawable switchgear contacts.
Blade-Type Contact Fingers with Racking Mechanism
Latest blade-type contact finger designs typically require a manual or motorized racking mechanism. These low voltage withdrawable switchgear contacts are designed to achieve high contact pressure while ensuring safe and controlled insertion and withdrawal.
Electrodynamic Force, High Current, and Temperature Rise Control
For high-current applications, low voltage withdrawable switchgear contacts must consider electrodynamic force effects. Key design considerations include:
Electrodynamic force-assisted clamping structures
Accurate calculation of electrodynamic parameters
Multi-contact finger coordination for uniform current distribution
Minimization of contact deviation
Effective temperature rise and power loss control
Proper design of low voltage withdrawable switchgear contacts ensures that electrodynamic forces enhance, rather than compromise, contact stability during short-circuit conditions.
High-Reliability Contact Solutions for Critical Applications
We specialize in the design and manufacture of low voltage switchgear systems for high-reliability applications. Our low voltage withdrawable switchgear contacts are engineered to meet the demanding requirements of:
Industrial power distribution systems
Intelligent manufacturing parks
Critical infrastructure projects
High-reliability electrical environments
By optimizing contact structure, surface treatment, electrodynamic force calculations, and multi-contact synchronization, our low voltage withdrawable switchgear contacts effectively address common industry challenges such as contact misalignment and excessive temperature rise.
Honcon provide customized low voltage withdrawable switchgear contacts and complete low voltage switchgear solutions, certified to core industry standards. Our solutions help ensure safe, stable, and long-term operation for modern power distribution systems.
Withdrawable switchgear contacts are primary electrical connectors that link withdrawable units to the main busbar in low voltage switchgear, ensuring reliable current transmission and safe operation.
Overheating is commonly caused by poor installation, insufficient contact pressure, contact misalignment, surface oxidation, or increased contact resistance due to wear and improper maintenance.
Electrodynamic forces generated during high current or short-circuit events can increase contact clamping force, helping improve short-circuit withstand capability and contact stability.
While not mandatory for all industrial applications, 50kA / 1s tests provide additional safety margin and demonstrate superior contact and mechanical design quality.
Yes. Customized withdrawable contact designs can be developed based on system current ratings, short-circuit levels, cabinet type, and project-specific reliability requirements.